Uterine Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Cancer, the unusual multiplication of cells, is a dreadful disease. The name in itself is enough to give chills down the spine. The most unfortunate thing is that the instances of cancer are skyrocketing in the last few decades. The malignancy which is affecting women the most is uterine cancer.
Uterine Cancer, also known as endometrial cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. The incidences of uterine cancer in women are increasing with each passing day. There are many factors that are to be blamed, like obesity and ignorance. Women tend to ignore their health unless it becomes a major, life- threatening issue. All women need is a little awareness and knowledge about uterine cancer and they will be able to keep this dreadful disease at bay.
So, here we are, lending a helping hand, to bring in light, the common and fatal uterine cancer.
What is uterine cancer?
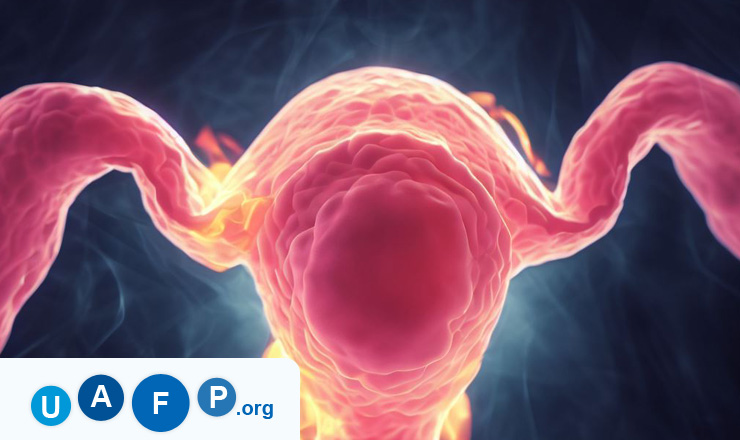
Before I tell you, what uterine cancer is, let’s understand what a uterus is? A uterus is a hollow organ which forms a major part of female reproductive system. It is located in the pelvis. This is the place where foetus grows.
Uterine cancer may occur in any part of uterus. It usually occurs in the inner lining of the uterus, i.e., endometrium and hence the name endometrial cancer.
A uterine tumour can be of two types:
- Benign, which is not cancerous in nature and hence, not life-threatening.
- Malignant, which is cancerous in nature and hence, can take a toll on life.
A malignant cancer, is quite dangerous. The cancerous cells multiply rapidly, break the wall of uterine tumour and can spread to other parts too.
Risk Factors
- Obesity
Obese women are more susceptible to uterine cancer.
- Endometrial Hyperplasia
An abnormal multiplication of the endometrium (lining of uterus) increases the risk of uterine cancer.
- Menstrual History
Women with menstrual irregularity are at a greater risk of developing uterine cancer. If a women had her first period before the age of 12 year and menopause after 55 years of age, she is susceptible to develop uterine cancer.
- Reproductive History
The woman who had never had children is also at a higher risk of uterine cancer.
- Radiation Therapy
Women who had radiation therapy to pelvic area are susceptible to endometrial cancer.
- Family History
Women with family history of uterine cancer may also develop uterine cancer.
- History of Estrogen
Women who used estrogen alone, without progesterone, are susceptible to endometrial cancer.
- Drug History
Women who consumed Tamoxifen to prevent or as a treatment of breast cancer, are at a higher risk of uterine cancer.
Symptoms Of Uterine Cancer
- The most common symptom is abnormal vaginal bleeding, discharge or spotting, which is quite abnormal after menopause.
- Pain while having sex.
- Pain or difficulty in urinating.
- Pain in the pelvic region.
The symptoms may be due to uterine cancer or may be because of other health issue. When any woman experiences any such symptom, she should immediately fix an appointment with her doctor, so as to diagnose the actual disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be done by:
- A thorough pelvic examination
- Ultrasound
- Biopsy
Treatment
The treatment options are:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Hormone Therapy
Is uterine cancer very curable?
The curability of uterine cancer depends on several factors, including the stage at which it is diagnosed, the type of uterine cancer, and the overall health of the patient. Generally, uterine cancer is often detected at an early stage because it tends to produce noticeable symptoms, such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, which prompts women to seek medical attention.
The most common type of uterine cancer is endometrial cancer, which typically has a better prognosis compared to other types like uterine sarcoma. The overall five-year survival rate for endometrial cancer is relatively high when diagnosed at an early stage, often exceeding 90%. However, if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, the prognosis may be less favorable.
Treatment options for uterine cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's individual circumstances.
Regular gynecological check-ups and early detection are crucial for improving the chances of a cure. If you suspect you may be at risk for uterine cancer or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate management. Remember that advances in cancer research and treatment continue to improve outcomes for those diagnosed with uterine cancer, so individual outcomes can vary based on many factors.
Can you live a long life after uterine cancer?
Yes, it is possible to live a long and healthy life after being diagnosed and treated for uterine cancer, especially if the cancer is detected at an early stage and responds well to treatment. The prognosis for uterine cancer varies depending on several factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, the effectiveness of the treatment, and the individual's overall health.
Here are some key factors that can influence long-term survival and quality of life for individuals with uterine cancer:
- Early Detection: Uterine cancer often presents with symptoms, such as abnormal vaginal bleeding, that prompt early medical attention. Detecting the cancer at an early stage typically leads to a better prognosis.
- Stage of Cancer: The stage at which uterine cancer is diagnosed plays a significant role in prognosis. In general, the earlier the stage, the better the chances of long-term survival.
- Treatment: The choice of treatment and its effectiveness are crucial factors. Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy can be used alone or in combination, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
- Overall Health: The patient's overall health and ability to tolerate treatment also impact outcomes. Healthy individuals often have a better chance of coping with treatment and recovering well.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence or potential long-term side effects of treatment.
- Lifestyle Factors: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, not smoking, and managing stress, can contribute to overall well-being and a better prognosis.
It's important to note that every individual's experience with uterine cancer is unique, and outcomes can vary. Advances in cancer research and treatment continue to improve the prognosis for those diagnosed with uterine cancer, and many individuals go on to live long, fulfilling lives after successful treatment.
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with uterine cancer, it's crucial to work closely with a medical team specializing in gynecologic oncology, follow the recommended treatment plan, and maintain regular follow-up care to optimize the chances of a positive long-term outcome.




